1. Overview
Thermal expansion is the tendency of materials to change dimensions in response to temperature changes. In pipeline and process systems, unaccommodated thermal expansion causes equipment damage, flange leaks, and pipe buckling.
Pipelines
Expansion Loops
Above-ground and buried lines require expansion accommodation to prevent overstress.
Storage Tanks
Freeboard
API 650 requires freeboard to prevent overfill from liquid expansion.
Piping Systems
Flexibility Analysis
ASME B31.3 requires thermal stress analysis for process piping.
Equipment
Thermal Relief
Blocked-in equipment requires PSV sizing for thermal expansion.
Key Definitions
- Linear expansion coefficient (α): Length change per unit length per degree (in/in/°F)
- Volumetric expansion coefficient (β): Volume change per unit volume per degree (β ≈ 3α for solids)
- Thermal strain: ε = α × ΔT (dimensionless)
- Thermal stress: σ = E × α × ΔT (stress when expansion is restrained)
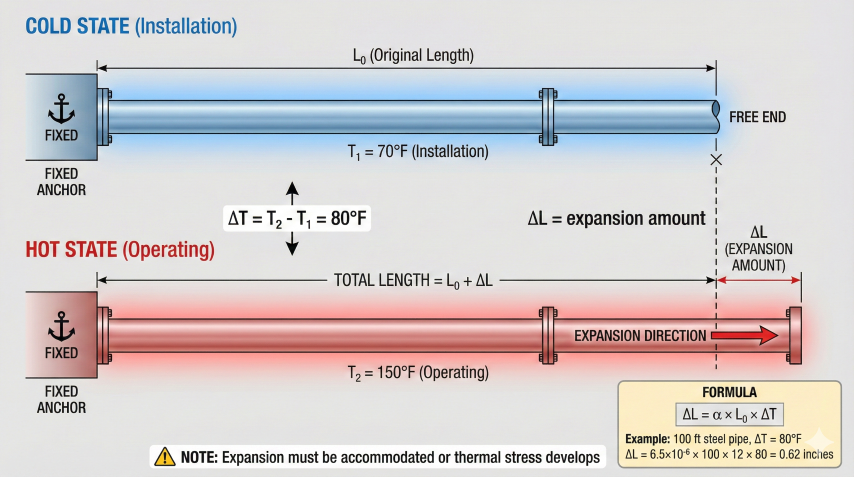
2. Linear Expansion
Linear thermal expansion describes length change with temperature. This is the primary concern for pipeline design and piping flexibility.
Calculation Example
Calculate expansion of 500-ft carbon steel pipeline with 150°F temperature increase:
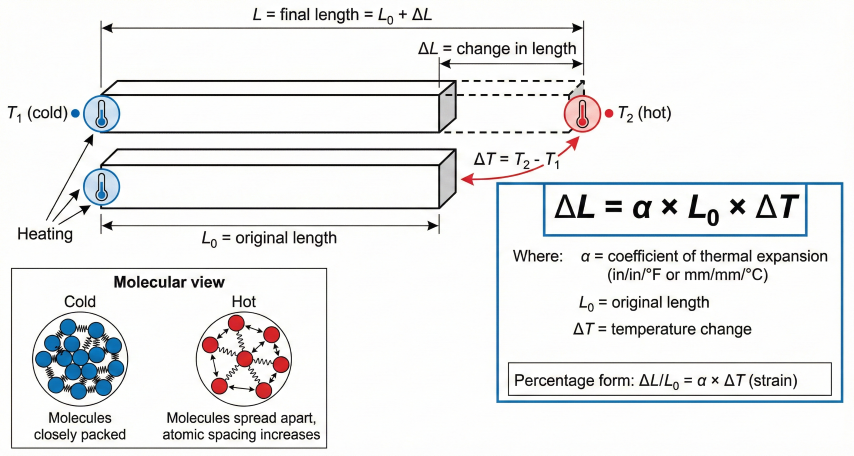
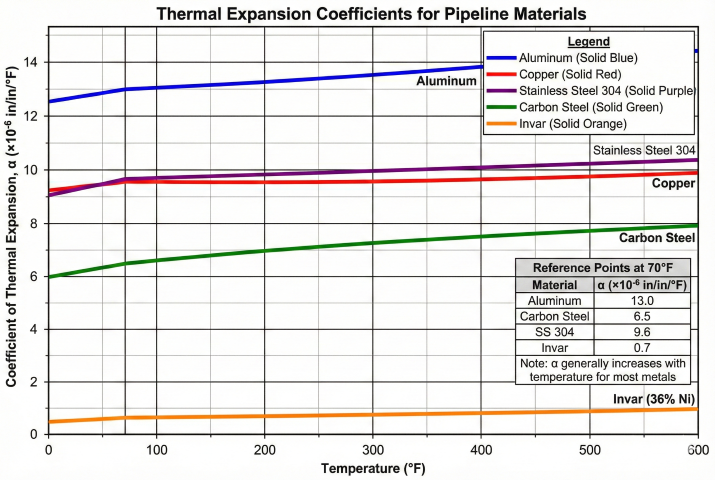
3. Expansion Coefficients
Expansion coefficients vary by material and temperature. Use mean coefficient over the operating temperature range for accurate calculations.
Common Piping Materials
| Material | α (×10⁻⁶ /°F) | Expansion per 100 ft per 100°F | E (×10⁶ psi) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel (A106) | 6.5 | 0.78 in | 29.0 |
| Stainless Steel 304 | 9.6 | 1.15 in | 28.3 |
| Stainless Steel 316 | 9.0 | 1.08 in | 28.0 |
| 9% Nickel (A353) | 7.0 | 0.84 in | 28.5 |
| Aluminum 6061 | 13.0 | 1.56 in | 10.0 |
| Copper | 9.8 | 1.18 in | 17.0 |
| PVC | 30.0 | 3.60 in | 0.4 |
| HDPE | 80.0 | 9.60 in | 0.11 |
Temperature-Dependent Coefficients (Carbon Steel)
For wide temperature ranges, use mean coefficient from ASME B31.3 Appendix C:
| Temperature Range (°F) | Mean α (×10⁻⁶ /°F) | Application |
|---|---|---|
| -20 to 200 | 6.3 | Typical gas pipelines |
| 70 to 300 | 6.5 | Standard process piping |
| 70 to 500 | 6.7 | Heated oil lines |
| 70 to 700 | 7.0 | High-temp process |
| 70 to 900 | 7.3 | Furnace piping, flares |
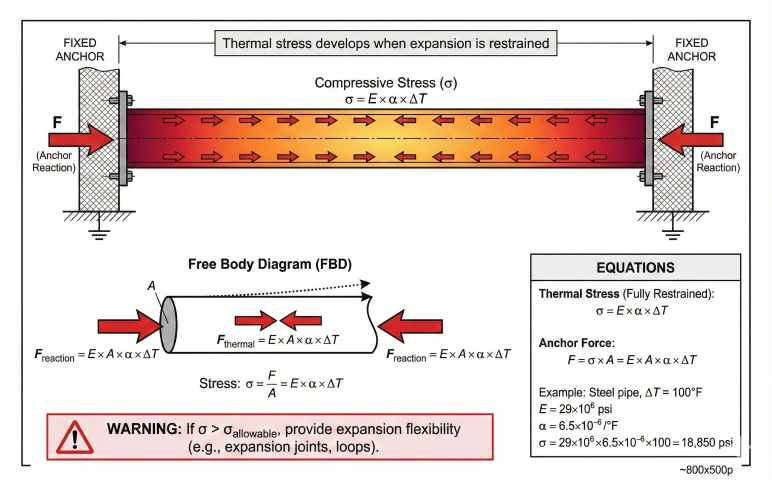
4. Thermal Stress Analysis
When thermal expansion is restrained, stresses develop. ASME B31 piping codes require flexibility analysis to ensure thermal stresses remain within allowable limits.
Allowable Stress Range (ASME B31.3)
Anchor Force Calculation
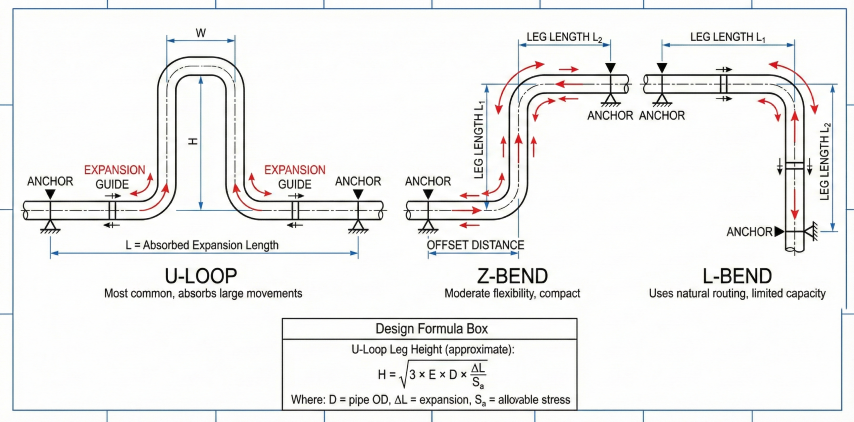
5. Expansion Loops & Flexibility
Expansion must be accommodated through piping flexibility, expansion loops, or mechanical expansion joints.
Expansion Loop Sizing
Expansion Accommodation Methods
| Method | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Natural flexibility (elbows) | No additional equipment; lowest cost | Requires sufficient routing flexibility |
| Expansion loops (U/Z shape) | Reliable; no moving parts; no maintenance | Requires space; adds pressure drop |
| Bellows expansion joints | Compact; high movement capacity | Requires anchors; limited life; maintenance |
| Ball joints | Handles large angular rotation | Expensive; limited pressure rating |
Support Types
| Support Type | Function | Thermal Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Anchor | Prevents all movement | Absorbs full thermal force—must be designed for high loads |
| Guide | Allows axial movement | Clearance must accommodate full expansion |
| Slide support | Allows lateral movement | Friction force = μ × Weight (μ ≈ 0.3 for PTFE) |
| Spring hanger | Supports weight with movement | Select spring range for thermal displacement |
6. Volumetric Expansion
Volumetric expansion is critical for liquid storage tanks, custody transfer calculations, and thermal relief valve sizing.
Liquid Expansion Coefficients
| Fluid | β (×10⁻⁴ /°F) | Volume Change per 10°F |
|---|---|---|
| Water (60°F) | 1.1 | 0.11% |
| Crude oil (API 30) | 4.0 | 0.40% |
| Gasoline | 6.8 | 0.68% |
| Diesel fuel | 5.0 | 0.50% |
| Propane (liquid) | 9.8 | 0.98% |
Tank Freeboard Calculation
Custody Transfer Impact
Volume measurement errors from temperature have significant financial impact:
Ready to use the calculator?
→ Launch Calculator