1. Overview
Accurate volume calculations ensure correct material ordering and prevent costly mid-pour shortages. Concrete is ordered in cubic yards (US) or cubic meters (metric).
Equipment pads
Compressors, pumps
Reinforced pads for dynamic loads.
Tank foundations
Ring walls, full pads
Support storage tanks.
Pipe supports
Piers, pedestals
Drilled shafts for pipelines.
Building slabs
Control rooms
Floor slabs for structures.
Units and Conversions
Waste Factors
| Application | Factor | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Formed walls | +5–10% | Precise forms |
| Slab on grade | +10–15% | Subgrade variation |
| Drilled piers | +15–20% | Over-drilling |
| Complex shapes | +15–20% | Irregular geometry |
2. Volume Formulas
Break complex shapes into simple geometries, calculate each, then sum. Always convert to cubic yards for ordering.
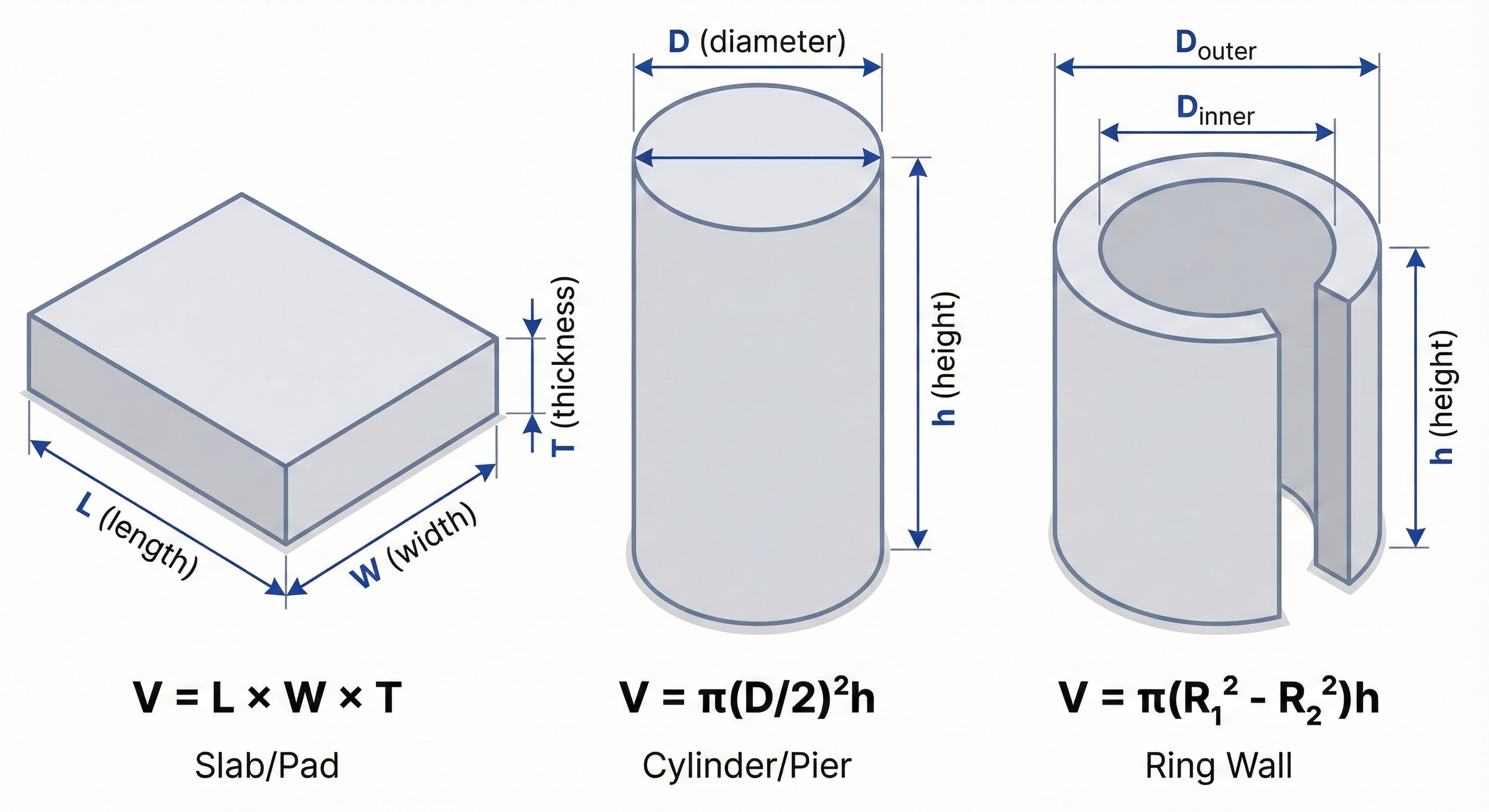
Rectangular Slab
Cylinder (Pier)
Ring Wall (Hollow Cylinder)
Footing with Wall
Formula Summary
| Shape | Formula |
|---|---|
| Rectangle | V = L × W × T |
| Cylinder | V = π r² h |
| Ring wall | V = π (R₁² − R₂²) h |
| Triangle prism | V = ½ b h L |
3. Equipment Foundations
Foundation size depends on equipment weight, soil capacity, and vibration requirements.
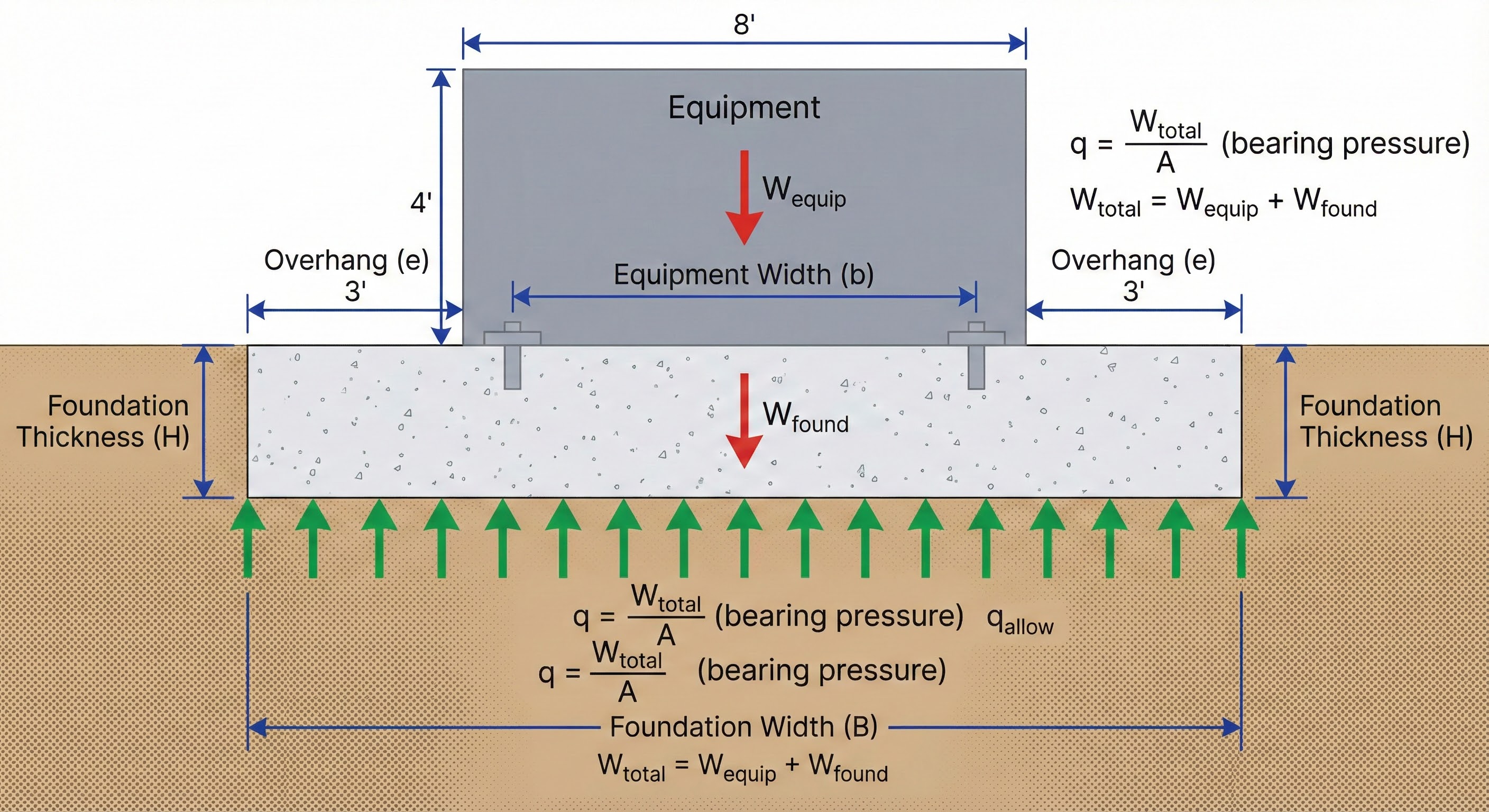
Sizing Criteria
Design Example
Tank Foundations
| Tank Size | Foundation Type | Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| < 20 ft dia | Full pad, 6–12 in | 1–5 yd³ |
| 20–50 ft dia | Ring wall + fill | 5–20 yd³ |
| > 50 ft dia | Ring wall | 20–100 yd³ |
Pipe Support Piers
4. Reinforcement
Rebar provides tensile strength and crack control. Quantities estimated from steel ratios or bar schedules.
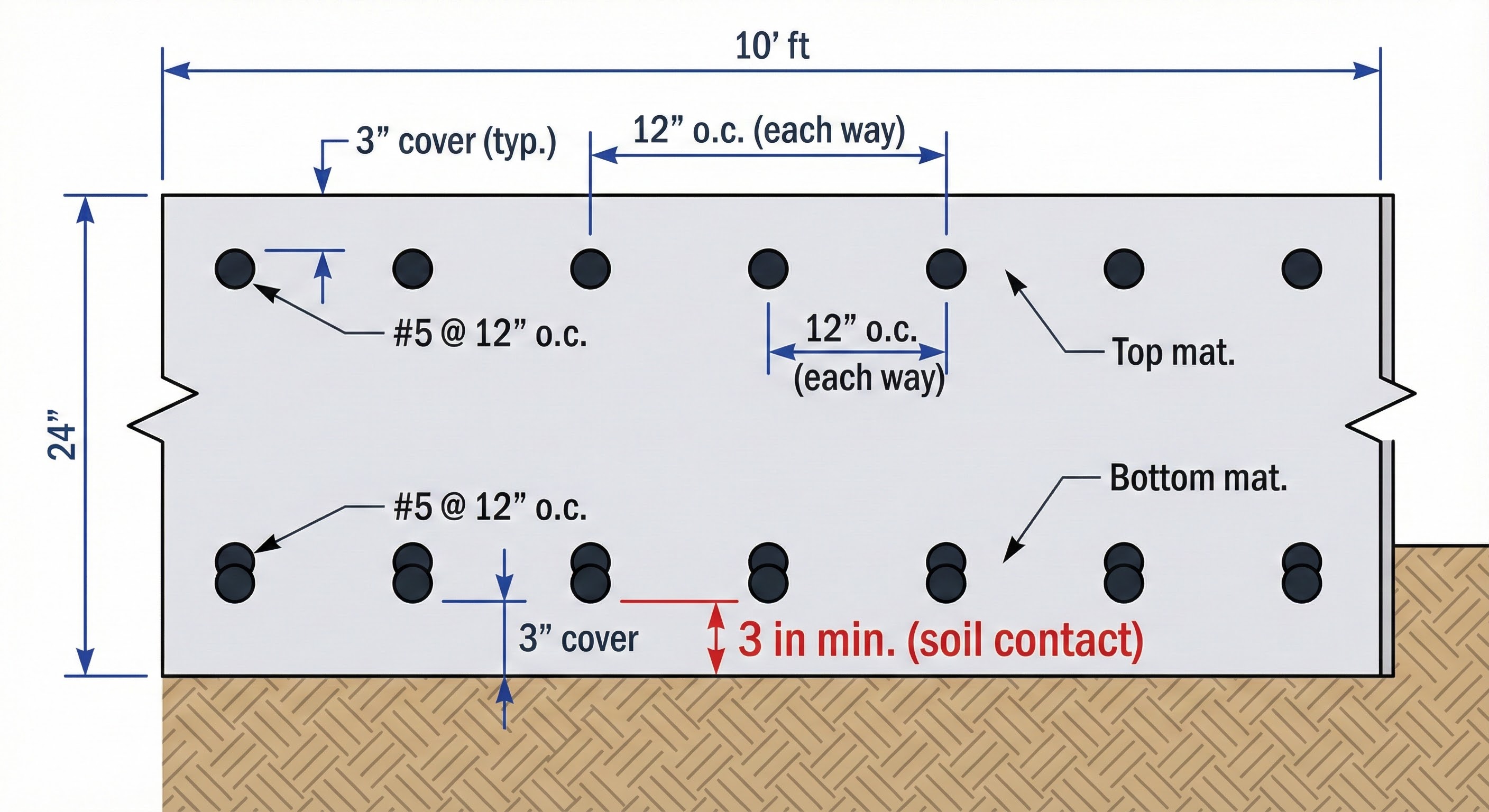
Reinforcement Ratios
Rebar Sizes
| Bar | Dia (in) | Weight (lb/ft) | Area (in²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| #3 | 0.375 | 0.376 | 0.11 |
| #4 | 0.500 | 0.668 | 0.20 |
| #5 | 0.625 | 1.043 | 0.31 |
| #6 | 0.750 | 1.502 | 0.44 |
| #7 | 0.875 | 2.044 | 0.60 |
| #8 | 1.000 | 2.670 | 0.79 |
Concrete Mix Specifications
| Strength | Application |
|---|---|
| 3,000 psi | Light-duty, non-structural |
| 4,000 psi | Standard foundations |
| 5,000 psi | Heavy equipment, high loads |
| 6,000+ psi | Special applications |
5. Field Practices
Pre-Pour Checklist
- Verify formwork dimensions match drawings
- Check rebar size, spacing, cover, and lap splices
- Confirm anchor bolt locations and projections
- Ensure subgrade is compacted and not frozen
- Coordinate truck arrival schedule
Temperature Requirements
| Condition | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Cold weather (< 40°F) | Heat materials, insulate, maintain 50°F min for 3–7 days |
| Hot weather (> 85°F) | Cool mix, add retarder, max 90°F at placement |
| Normal | Begin curing immediately, maintain moist 7 days |
Common Issues
| Problem | Cause | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Cracking | Shrinkage, poor curing | Control joints, proper curing |
| Honeycomb | Poor vibration | Proper consolidation |
| Cold joints | Pour delay | Continuous placement |
| Scaling | Freeze-thaw | Air entrainment |
Ready to use the calculator?
→ Launch Calculator