Flow Assurance
Inhibitor Injection Rate
Calculate hydrate inhibitor dosing using Hammerschmidt equation for methanol and glycol systems.
1. Hammerschmidt Equation
Predicts hydrate temperature depression based on inhibitor concentration in the aqueous phase.
Hammerschmidt Equation:
ΔT = K × W / (M × (100 - W))
Solved for concentration:
W = 100 × M × ΔT / (K + M × ΔT)
Where:
ΔT = Hydrate temperature depression (°F)
K = Inhibitor constant (see table)
W = Weight % inhibitor in aqueous phase
M = Molecular weight of inhibitor
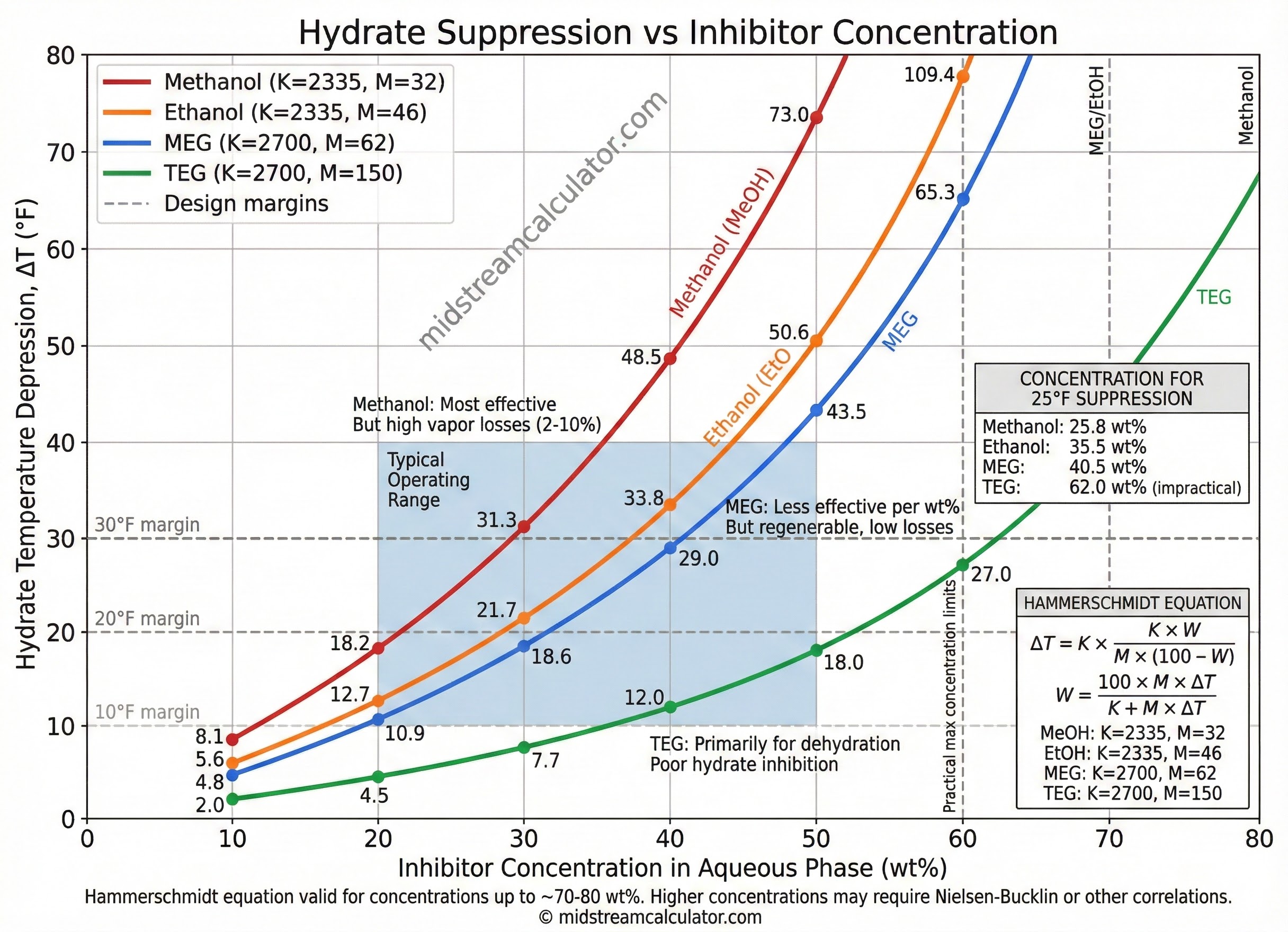
Inhibitor Constants
| Inhibitor | MW | K | Max W | ΔT @ 25 wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methanol | 32.04 | 2,335 | ~80% | 24.3°F |
| Ethanol | 46.07 | 2,335 | ~70% | 16.9°F |
| MEG | 62.07 | 2,700 | ~70% | 14.5°F |
| DEG | 106.12 | 2,700 | ~65% | 8.5°F |
| TEG | 150.17 | 2,700 | ~60% | 6.0°F |
Example: Methanol Concentration
Given: Need 30°F hydrate suppression using methanol
K = 2,335, M = 32.04
W = 100 × 32.04 × 30 / (2,335 + 32.04 × 30)
= 96,120 / 3,296
= 29.2 wt% methanol in aqueous phase
2. Methanol Injection
Methanol is effective but lost to both gas and liquid hydrocarbon phases. Total requirement = aqueous + gas losses + HC losses.
Total methanol requirement:
MeOH_total = MeOH_water + MeOH_gas + MeOH_HC
In aqueous phase (Hammerschmidt):
MeOH_water = W × W_rate / (100 - W) [lb/day]
Lost to gas phase:
MeOH_gas = Kᵥ × P × Q_gas [lb/day]
Where Kᵥ = vapor distribution factor (see table)
Lost to hydrocarbon liquid:
MeOH_HC ≈ 0.5-2% of condensate volume
Methanol Vapor Loss Factor (Kᵥ)
| T (°F) | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kᵥ (lb/MMSCF/psi) | 0.0015 | 0.0022 | 0.0032 | 0.0045 | 0.0062 |
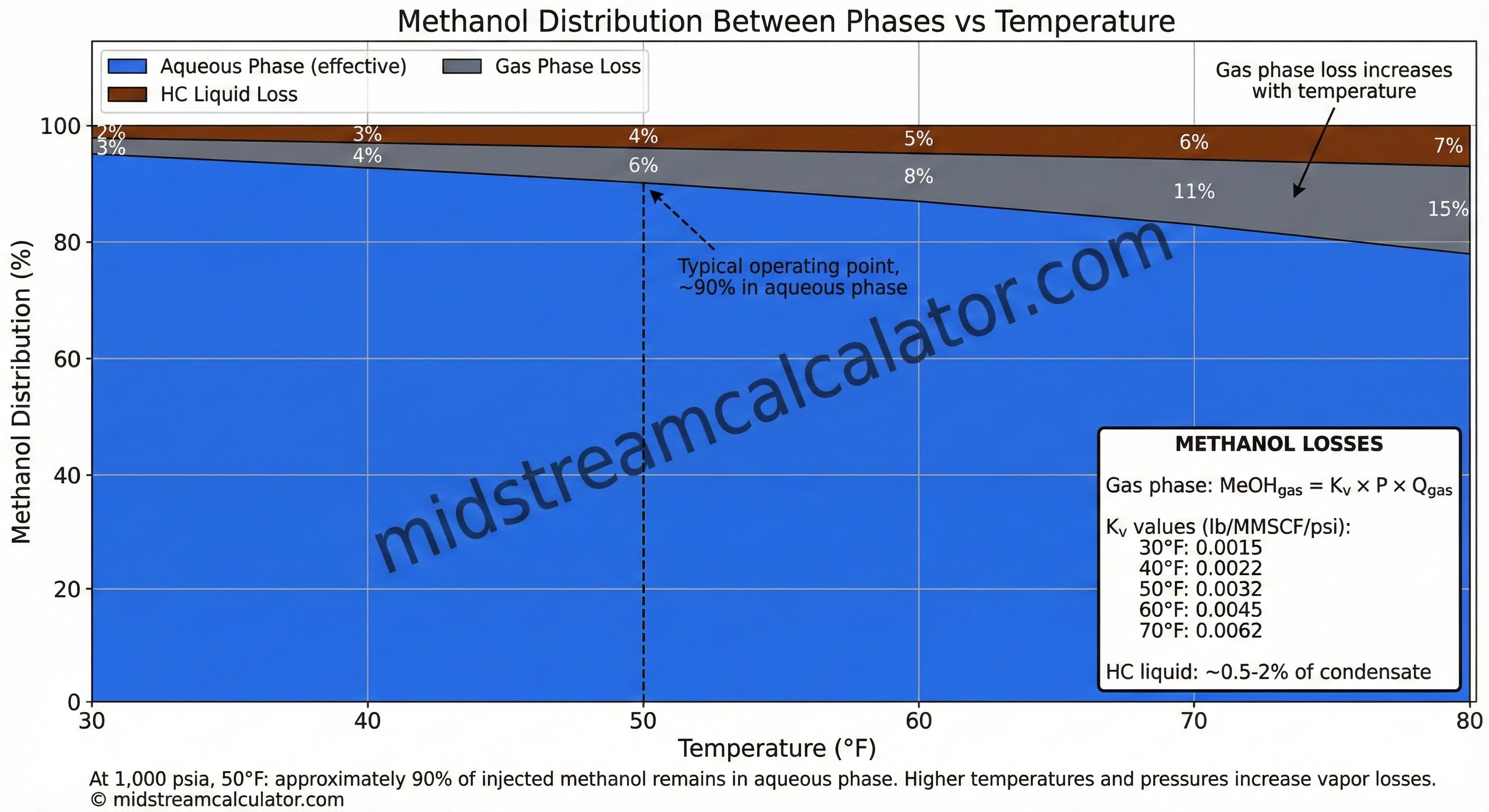
Example: Methanol Injection Rate
Given: 10 MMSCFD, 50 bbl/day water, 1000 psia, 40°F
Need 25 wt% MeOH in water
Water mass: 50 bbl × 350 lb/bbl = 17,500 lb/day
MeOH in water:
= 0.25 × 17,500 / (1 - 0.25) = 5,833 lb/day
MeOH to gas (Kᵥ = 0.0022 at 40°F):
= 0.0022 × 1000 × 10 = 22 lb/day
Total: 5,855 lb/day ÷ 6.6 lb/gal = 887 gal/day (21 bbl/day)
⚠ Safety: Methanol is toxic and flammable. Follow applicable handling codes.
3. Glycol (MEG) Injection
Glycols are preferred for pipelines because they're regenerable with minimal vapor losses.
MEG vs Methanol
| Factor | Methanol | MEG |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness (ΔT per wt%) | Higher | Lower |
| Recovery | Usually lost | Regenerated (80-90%) |
| Vapor loss | 2-10% | <0.1% |
| HC solubility loss | 1-2% | <0.5% |
| Cost driver | Operating (makeup) | Capital (regen unit) |
| Best application | Short-term, remote | Long pipelines, offshore |
Glycol Injection Calculation
Lean glycol injection rate:
G_lean = W_water × C_rich / (C_lean - C_rich)
Rich glycol concentration:
C_rich = 100 × M × ΔT / (K + M × ΔT) [from Hammerschmidt]
Where:
G_lean = Lean glycol rate (lb/day)
W_water = Water production (lb/day)
C_lean = Lean glycol concentration (typically 80-90 wt%)
C_rich = Rich glycol concentration (from required ΔT)
Example: MEG Injection Rate
Given: 100 bbl/day water, need 25°F suppression
Lean MEG = 85 wt%, M = 62.07, K = 2,700
Rich MEG concentration (Hammerschmidt):
C_rich = 100 × 62.07 × 25 / (2,700 + 62.07 × 25)
= 155,175 / 4,252 = 36.5 wt%
Water mass: 100 bbl × 350 lb/bbl = 35,000 lb/day
Lean MEG rate:
G_lean = 35,000 × 36.5 / (85 - 36.5)
= 1,277,500 / 48.5 = 26,340 lb/day
Volume: 26,340 lb ÷ 9.3 lb/gal = 2,833 gal/day (67 bbl/day)
4. Corrosion Inhibitors
Film-forming corrosion inhibitors protect against CO₂ and H₂S attack. Dosing is typically ppm-based on produced water volume.
Dosing Rates
| Application | Typical Rate (ppm) |
|---|---|
| Sweet gas (CO₂ only) | 10-25 |
| Sour gas (H₂S present) | 25-50 |
| High CO₂ (>5 mol%) | 50-100 |
| Produced water systems | 25-75 |
Injection Rate Calculation
Continuous injection:
Rate (gal/day) = Q_water (bbl/day) × ppm × 42 / (ρ × 10⁶)
Where:
Q_water = Water production rate (bbl/day)
ppm = Target concentration
ρ = Inhibitor density (lb/gal), typically 8-9
42 = gal/bbl
Example:
500 bbl/day water, 50 ppm, ρ = 8.5 lb/gal
Rate = 500 × 50 × 42 / (8.5 × 10⁶) = 0.12 gal/day
References
- GPSA Engineering Data Book, Section 20
- NACE SP0106 – Internal Corrosion Control
- API RP 14E – Offshore Platform Piping
Ready to calculate?
→ Inhibitor Injection Rate Calculator