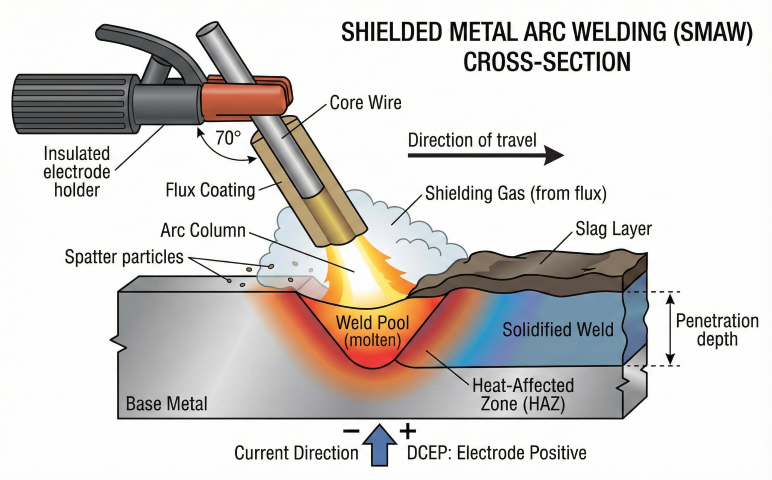
1. Overview
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) uses flux-coated consumable electrodes. The flux generates shielding gas, forms protective slag, stabilizes the arc, and adds alloying elements. Electrode selection directly impacts weld quality and mechanical properties.
Key Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Minimum weld metal tensile (ksi). Must meet or exceed base metal SMYS. |
| Deposition Efficiency | Deposited weld metal / consumed electrode weight (58-75% typical). |
| Low-Hydrogen | Electrodes with <8 ml H₂/100g. Required for thick sections (>0.5") and high-strength steel. |
| Polarity | DCEP: deeper penetration. DCEN: faster deposition. AC: alternating. |
| Position | 1G (flat), 2G (horizontal), 3G (vertical), 4G (overhead). All-position = any. |
Common Selection Errors
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen cracking | High-H electrode on thick/high-CE steel | E7018 (low-H) + preheat |
| Strength mismatch | E6010 on X70 pipe | E8018-G (80 ksi tensile) |
| Poor root fusion | E7018 for root pass | E6010 for penetration |
| Porosity | Wet low-H electrodes | Store at 250-300°F |
2. AWS Classification System
AWS A5.1-2012 (carbon steel) and A5.5-2014 (low-alloy steel) standardize electrode naming. Each digit conveys specific properties.
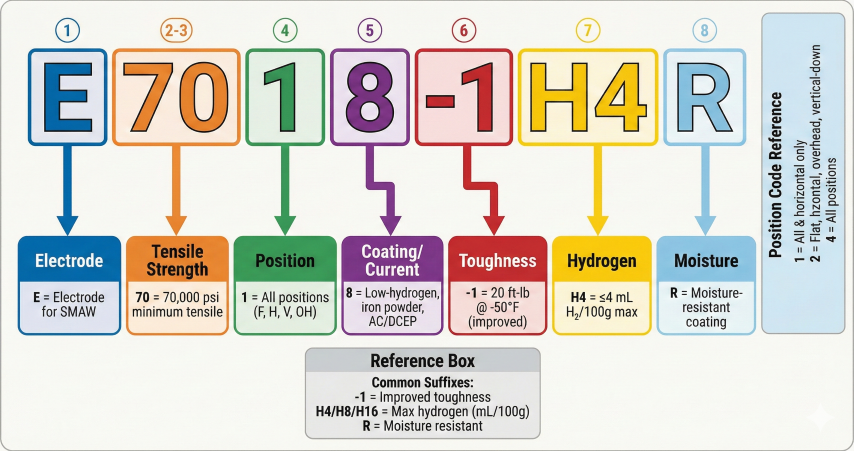
Alloy Suffixes (AWS A5.5)
| Suffix | Alloy | Service |
|---|---|---|
| -C1 | 2.5% Ni | Low temp to -50°F |
| -C2 | 3.5% Ni | Cryogenic to -75°F (LNG) |
| -G | Unspecified | General purpose high-strength |
| H4 | — | <4 ml H₂/100g (extra low-H) |
| H8 | — | <8 ml H₂/100g (standard low-H) |
| R | — | Moisture-resistant coating |
Mechanical Properties by Classification
| Electrode | Tensile | Yield | Elong. | Base Metal Match |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E6010/E6011 | 62 ksi | 50 ksi | 22% | A36, X42-X52 |
| E7018 | 72 ksi | 60 ksi | 22% | A572 Gr 50, X52-X60 |
| E8018-G | 80 ksi | 68 ksi | 19% | X70 pipeline |
| E9018-G | 90 ksi | 78 ksi | 17% | X80 pipeline |
| E10018-D2 | 100 ksi | 87 ksi | 16% | X100, HY-100 |
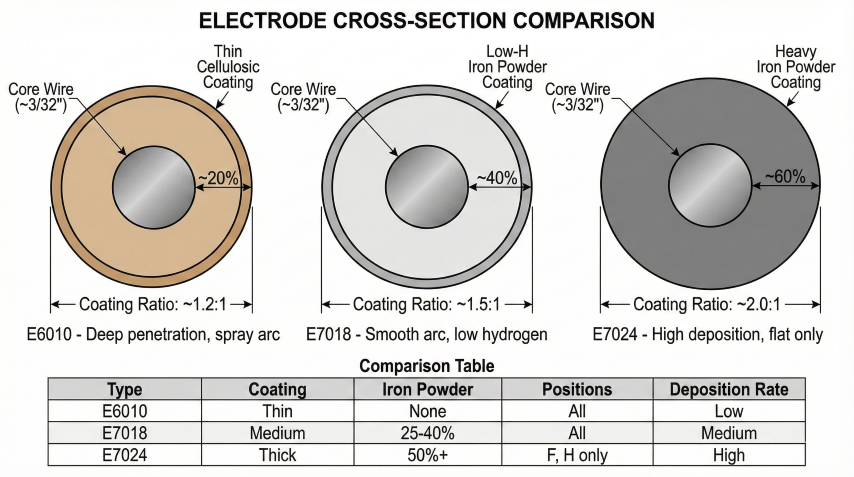
3. Common Electrode Types
E6010 — Pipeline Root Pass
High cellulose sodium coating provides deep penetration for root passes. Fast-freezing puddle enables vertical-down welding on cross-country pipelines.
E7018 — Low-Hydrogen Standard
Workhorse for structural and pipeline fill/cap. Low hydrogen (<8 ml/100g) prevents cracking. Requires strict moisture control.
Deposition Efficiency
| Electrode | Efficiency | Coating | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| E6010 | 58% | Cellulosic | Root passes |
| E6013 | 65% | Titania | Sheet metal |
| E7018 | 68% | Low-H iron powder | Fill/cap passes |
| E7024 | 75% | High iron powder | Flat production |
| E8018-G | 68% | Low-H iron powder | X70 pipeline |
4. Selection Criteria
Strength Matching
Weld metal tensile must meet or exceed base metal SMYS. Target overmatch ratio: 1.2-1.4×.
Hydrogen Cracking Prevention
HIC occurs when hydrogen diffuses into HAZ. Control: hydrogen source, microstructure, and restraint.
Preheat Table (ASME B31.8)
| Wall | Ambient >50°F | 32-50°F | <32°F |
|---|---|---|---|
| <0.500" | None | 50°F | 100°F |
| 0.500-0.750" | 50°F | 100°F | 200°F |
| 0.750-1.000" | 175°F | 200°F | 250°F |
| >1.000" | 250°F | 275°F | 300°F |
Low-H required for t >0.750", SMYS >52 ksi, or prior cracking.
5. Pipeline Welding (API 1104)
Cross-country pipeline construction uses E6010 root passes and E7018 fill/cap. Standardized per API 1104.
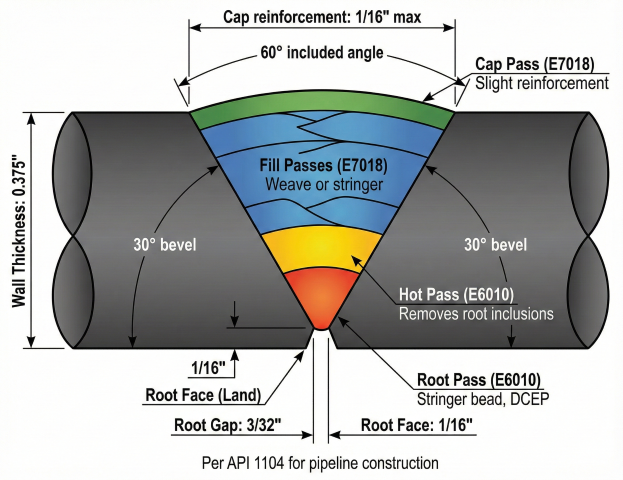
Electrode Consumption
| Pipe | Wall | Root | Fill/Cap | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12" OD | 0.375" | 4-5 rods | 8-10 rods | ~1.5 lb |
| 24" OD | 0.500" | 8-10 rods | 18-22 rods | ~3.5 lb |
| 36" OD | 0.625" | 12-15 rods | 35-45 rods | ~6.5 lb |
Common Defects
| Defect | Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Incomplete penetration | Low current | Increase amps, proper fit-up |
| Porosity | Moisture | Dry electrodes, clean surface |
| Slag inclusion | Poor cleaning | Wire brush each pass |
| Undercut | High current | Reduce amps, pause at edges |
| HIC cracking | Hydrogen | Low-H, preheat, slow cool |
6. Storage & Handling
Proper storage prevents moisture contamination—the primary cause of porosity and hydrogen cracking with low-H electrodes.
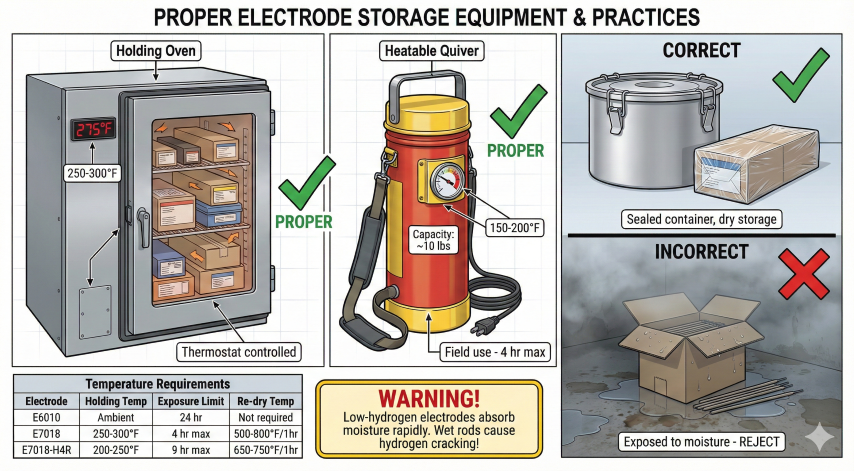
Storage Requirements
| Electrode | Storage | Exposure | Re-dry |
|---|---|---|---|
| E6010/E6011 | Ambient dry | N/A | Not required |
| E7018 | 250-300°F | 4 hours | 700-800°F × 1 hr |
| E7018-H4R | 250-300°F | 9 hours | 650-750°F × 1 hr |
| E8018/E9018 | 250-300°F | 4 hours | 700-800°F × 1 hr |
| E10018/E11018 | 300-350°F | 2 hours | 800-850°F × 2 hr |
Field Practices
- Issue 1-2 lb/welder to minimize exposure
- Heated quivers: 150-200°F for field work
- Return unused: Back to oven within exposure limit
- Inspect coatings: Discard if cracked or chipped
Applicable Codes
| Code | Scope |
|---|---|
| AWS A5.1-2012 | Carbon steel electrodes (E60XX, E70XX) |
| AWS A5.5-2014 | Low-alloy electrodes (E80XX+) |
| API 1104 | Pipeline welding, WPS qualification |
| ASME B31.8 | Gas transmission piping, preheat |
| AWS D1.1 | Structural welding |
Ready to use the calculator?
→ Launch Calculator